Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) vs Vaginal Infections: Differences, Symptoms, Treatments
Many people experience discomfort in the genital area at some point in their lives, and such discomfort can often indicate an infection. Two common infections in this area are urinary tract infections (UTIs) and vaginal infections, including bacterial vaginosis (BV) and yeast infections. Although these infections are distinct, some of their symptoms may overlap, which can make them confusing to differentiate.
UTIs affect the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys, while vaginal infections affect the vagina and surrounding area. Understanding the difference between these infections is important because their treatments vary. This article will explore their causes, symptoms, treatments, and how to prevent them.
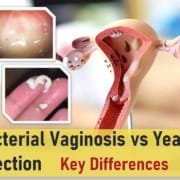
Difference Between a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) and Vaginal Infection
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): UTIs affect the urinary system, which includes the bladder, kidneys, urethra, and ureters. They are typically caused by bacteria, with E. coli being the most common culprit. UTIs generally cause pain during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Severe cases may result in fever or kidney infection.
Vaginal Infections: Vaginal infections include yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and trichomoniasis. They affect the vaginal area and may cause itching, burning, and abnormal discharge. Each type of vaginal infection has different causes; yeast infections are caused by overgrowth of the Candida fungus, while bacterial vaginosis results from an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina.
Can You Have Both UTI and Vaginal Infection at the Same Time?
Yes, it is possible to have both a UTI and a vaginal infection simultaneously. In fact, treating a UTI with antibiotics can sometimes lead to a vaginal infection, particularly a yeast infection, as antibiotics disrupt the balance of normal bacteria in the vagina. Furthermore, having bacterial vaginosis may increase the likelihood of recurrent UTIs due to bacteria migrating from the vagina to the urinary tract.
Causes of UTIs and Vaginal Infections
Causes of UTIs:
- Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, leading to infection.
- Improper hygiene: Wiping from back to front after using the bathroom can transfer bacteria to the urethra.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can result in infrequent urination, which allows bacteria to multiply in the bladder.
Causes of Vaginal Infections:
- Yeast infections: Overgrowth of the Candida fungus can occur due to antibiotic use, high sugar intake, or hormonal changes.
- Bacterial vaginosis: An imbalance in vaginal bacteria, often triggered by douching or new sexual partners, leads to BV.
- Trichomoniasis: This sexually transmitted infection (STI) is caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis.
Symptoms of UTIs and Vaginal Infections
Symptoms: How to Tell the Difference
Although both UTIs and vaginal infections cause discomfort in the genital area, their symptoms differ significantly:
| Symptom | UTI | Vaginal Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Painful urination | Common | Possible, especially with yeast infections |
| Frequent urination | Very common | Rare |
| Abdominal pain | Common in severe cases | Rare |
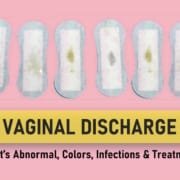
| Abnormal discharge | None | Thick, milky discharge (yeast infection); thin, gray discharge with fishy odor (BV) |
| Itching or burning | Sometimes | Very common, especially with yeast infections |
| Fever | Possible in severe cases | Rare |
Symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Persistent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. The urinary system is designed to keep bacteria out, but sometimes these defenses fail, resulting in an infection.
Symptoms of Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
- Unusual odor, especially after sex
- Excessive grayish-white vaginal discharge
- Burning when urinating
- Itching around the vagina
Bacterial vaginosis occurs when the balance of bacteria in the vagina becomes disrupted. This condition is not classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) but can occur in women who are not sexually active.
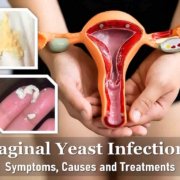
Symptoms of a Vaginal Yeast Infection
- Severe vaginal itching
- Irritated skin around the vagina
- Pain while urinating or during sexual intercourse
- Thick, white, clumpy, and odorless vaginal discharge
Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast, which is naturally present in the body. This overgrowth can be triggered by factors such as antibiotic use, high estrogen levels, diabetes, or a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
- Greenish-yellow vaginal discharge with a strong odor
- Vaginal itching or irritation
- Painful intercourse
- Discomfort during urination
- Vaginal bleeding
- Lower abdominal pain
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. An oral prescription is required to treat this condition.
Causes of UTIs and Vaginal Infections
Causes of UTIs
Most UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract through the urethra. In sexually active women, about 80% of UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria. Recent research suggests that the vaginal bacterium Gardnerella vaginalis can also trigger dormant E. coli in the bladder to cause recurrent UTIs. In rare cases, UTIs can progress to more serious infections, such as kidney infections (pyelonephritis), which require immediate medical attention.
Causes of Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
BV occurs when there’s an imbalance between the “good” and “bad” bacteria that live in the vagina. Factors that can disrupt this balance include unprotected sex, douching, and hormonal changes.
Causes of Yeast Infections
Yeast infections occur when the normal bacteria that keep yeast in check become unbalanced. This imbalance allows an overgrowth of yeast, particularly Candida. Common causes include antibiotic use, pregnancy, high estrogen levels, diabetes, and a weakened immune system.
Causes of Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which is most commonly transmitted through sexual contact.

Treatment Options
Treatment for UTIs
The primary treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and fosfomycin. In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter (OTC) products like URIEXO can help relieve UTI symptoms such as frequent urination, painful urination, and pelvic pain.
It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is fully cleared. In severe cases, or if the UTI progresses to a kidney infection, intravenous antibiotics may be required.
Treatment for Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
BV can be treated with prescription antibiotics, such as metronidazole or clindamycin, in either oral or topical form. Over-the-counter (OTC) vaginal gels like GYNALAC are also available for treating and preventing BV.
Treatment for Yeast Infections
Yeast infections can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams, ointments, and suppositories, as well as oral antifungal prescriptions. Common OTC options include miconazole and clotrimazole, while fluconazole is a common oral prescription.
Treatment for Trichomoniasis
The only effective treatment for trichomoniasis is a prescription for an oral antibiotic, such as metronidazole or tinidazole.
Prevention Tips
Preventing UTIs
- Drink plenty of water to flush bacteria from your urinary tract.
- Urinate frequently and avoid holding urine for long periods.
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom to prevent bacteria from spreading.
- Urinating after sexual intercourse may help flush bacteria from the urethra.
- Avoid douching, which can upset the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina.
Preventing Vaginal Infections
- Maintain good hygiene by keeping the vaginal area clean and dry.
- Avoid using scented soaps, feminine sprays, or douches, which can irritate the vagina and disrupt the balance of bacteria.
- Wear breathable, cotton underwear to reduce moisture buildup.
- Practice safe sex by using condoms to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What’s the difference between a UTI and a yeast infection?
While both UTIs and yeast infections can cause discomfort during urination, UTIs primarily affect the urinary system, while yeast infections affect the vaginal area. UTIs often cause frequent urination and lower abdominal pain, while yeast infections lead to thick, white discharge and itching.
Can you have a UTI and a vaginal yeast infection at the same time?
Yes, it’s possible to have both at the same time. Treating a UTI with antibiotics can sometimes cause a yeast infection by disrupting the normal balance of bacteria in the vagina.
How can I tell if I have bacterial vaginosis (BV) or a UTI?
Bacterial vaginosis causes a thin, grayish discharge with a strong fishy odor, while a UTI typically does not cause discharge. UTIs mainly cause painful and frequent urination. If you’re unsure, a doctor can help diagnose the issue based on symptoms and lab tests.
What are the symptoms of kidney infection compared to a UTI?
A kidney infection, which is more severe than a UTI, may cause fever, chills, lower back pain, nausea, and vomiting. It can occur if a UTI spreads to the kidneys. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Can vaginal dryness cause a yeast infection?
While vaginal dryness itself doesn’t cause yeast infections, it can lead to irritation and small tears, making the area more susceptible to infections. Using lubricants and maintaining good hygiene can help prevent this.
Can a UTI turn into a kidney infection?
Yes, if a UTI is left untreated, it can spread to the kidneys, leading to a more serious infection called pyelonephritis. Kidney infections require immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between UTIs and vaginal infections is critical for proper diagnosis and treatment. While both conditions can cause discomfort and share some symptoms, they affect different parts of the body and require different treatment approaches. Prompt medical attention and effective prevention strategies can help reduce the risk of these infections. If you experience persistent symptoms or have recurrent infections, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate guidance and treatment options.
By staying informed and taking proactive steps, you can effectively manage and prevent UTIs and vaginal infections, maintaining better overall health and well-being.